跟练代码随想录之链表篇
写在前面,这个系列是跟着B站的代码随想录跟练算法的部分。算法还是比较薄弱,慢慢打基础吧,这篇文章很久以前就写好了,只是发布的时间比较晚了,最近也是打算迁移一下自己的文章。
友链到卡哥 https://www.programmercarl.com/
1.移除链表元素(leetcode203) 这题算是链表里比较基础的了,构建了链表的基本思想。
两种方法,1:头节点和中间节点分开处理,这样要先用一个while循环,找到第一个不为val 的节点,充当头节点;
2:声明一个虚拟节点dummyNode,其next指向头节点,然后直接一个while循环来判断,相等则删,不等则next;注意,判断的是当前节点的next,因为这是单向链表,我们想删next,需要有cur,我们想删cur,却没有cur的前一个节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public ListNode removeElements (ListNode head, int val) { ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode (); dummyNode.next = head; ListNode cur = dummyNode; while (cur!=null &&cur.next!=null ){ if (cur.next.val==val) cur.next = cur.next.next; else cur = cur.next; } return dummyNode.next; } }
2.设计链表(leetocde707) 这个设计还挺麻烦的,有很多小细节要注意,哪怕我看了卡尔的视频,但是还是debug了三次才ac。
我链表插入是没有问题的,主要的出bug的地方在 第53行,不能等于,因为size也可以添加到尾部;第66行,如果大于size要return null;第28行,语法错误,不能直接index。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 class MyLinkedList { class Node { int val; Node next; public Node () this .val=0 ; this .next=null; } public Node (int val) this .val = val; this .next = null; } } Node dummy; int size; public MyLinkedList () dummy = new Node (); size=0 ; } public int get (int index) if (index<0 ||index>=size) return -1 ; Node cur = dummy; while (index!=0 ){ cur = cur.next; index--; } return cur.next.val; } public void addAtHead (int val) Node head = new Node (val); head.next = dummy.next; dummy.next = head; size++; } public void addAtTail (int val) Node cur = dummy; while (cur.next!=null){ cur = cur.next; } Node newNode = new Node (val); cur.next = newNode; size++; } public void addAtIndex (int index, int val) if (index<0 ||index>size) return ; Node newNode = new Node (val); Node cur = dummy; while (index!=0 ){ cur = cur.next; index--; } newNode.next = cur.next; cur.next = newNode; size++; } public void deleteAtIndex (int index) if (index<0 ||index>=size) return ; Node cur = dummy; while (index!=0 ){ cur = cur.next; index--; } cur.next = cur.next.next; size--; } }
3.翻转链表(leetcode206) 这题讲的也是很清晰的,翻转链表的话是需要三个指针的;
因为我们是单链表,所以需要一个pre指针保留上一个位置,需要一个cur指针保存当前位置,但是为了能让循环遍历下去,我们需要一个temp指针来保留下一个位置,从而不断遍历。而循环终止条件我们可以模拟一下就是当cur等于空时,循环终止。
而递归的写法,其实就是参考双指针的写法来的,跟双指针一模一样,所以递归不是凭空想出来的,递归的过程就是循环的过程。
递归这里有个坑,在第52行,我们需要用一个值来接收下一层递归的返回值,不然我们第一层递归是拿不到下面层递归的返回值的,这里卡尔没讲清楚。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { if (head==null ) return null ; if (head.next==null ) return head; ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = head; ListNode temp = cur.next; while (cur!=null ){ temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } } class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode cur = head; ListNode pre = null ; return reverse(cur,null ); } public ListNode reverse (ListNode cur, ListNode pre) { if (cur == null ) return pre; ListNode temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; ListNode retNode = reverse(temp,cur); return retNode; } }
4.两两交换链表中的节点(leetcode24) 这题的话,还是注意一个虚拟头节点的使用吧,要操纵3个节点。
容易出现的问题就是空指针和死循环。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs (ListNode head) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode (); dummy.next = head; ListNode cur = dummy; while (cur.next!=null &&cur.next.next!=null ){ ListNode temp = cur.next; ListNode temp1 = cur.next.next.next; cur.next = cur.next.next; cur.next.next = temp; temp.next = temp1; cur = cur.next.next; } return dummy.next; } }
5.删除链表的倒数第N个节点(leetcode19) 这题的话主要是快慢指针的思想。以后看到找倒数的多少多少个,就想到快慢指针!
然后为什么用dummy,下面也讲了。统一性问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode (); dummy.next = head; ListNode fast = dummy; ListNode slow = dummy; n++; while (n--!=0 &&fast!=null ){ fast = fast.next; } while (fast!=null ){ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } slow.next = slow.next.next; return dummy.next; } } class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode cur = head; int size = 0 ; while (cur!=null ){ cur = cur.next; size++; } int pos = size+1 -n-1 ; ListNode dummy = new ListNode (); dummy.next = head; cur = dummy; while (pos--!=0 ){ cur = cur.next; } cur.next = cur.next.next; return dummy.next; } }
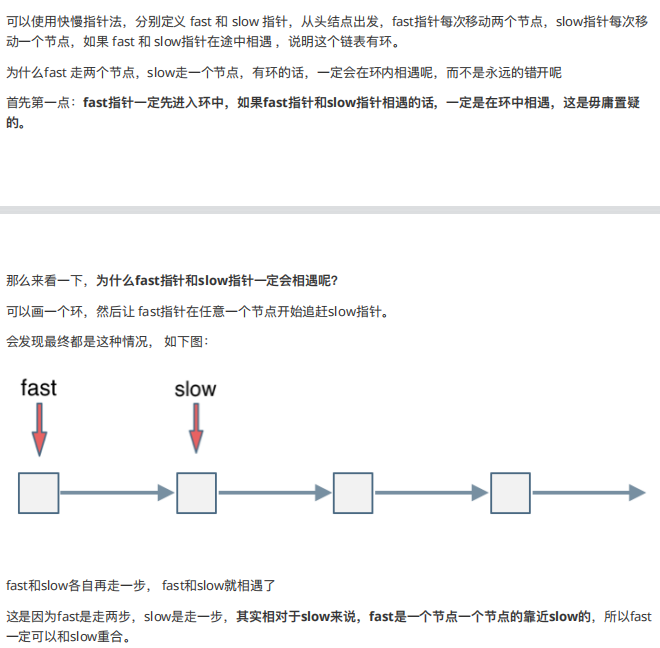
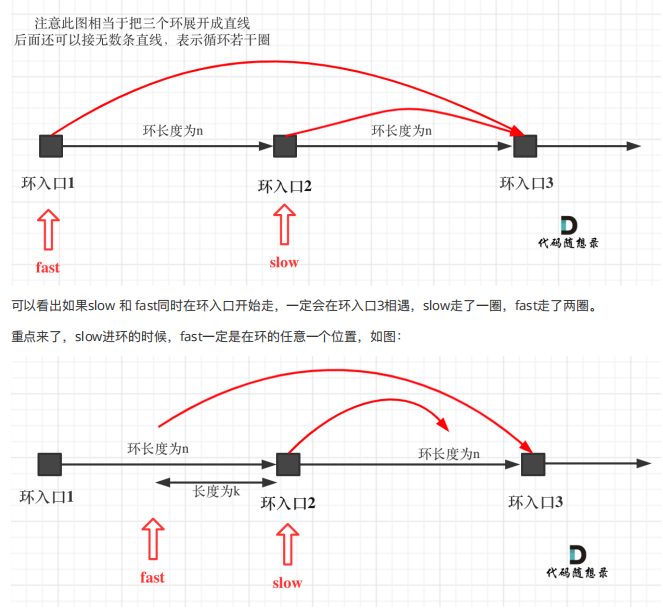
6.环形链表(leetcode142) 这个的话,有点难度。
有三个地方需要注意:
//如何判断有环:快慢指针
//如何判断入口处在那里:相遇起点追及证明(利用时间相等建立等式)
//为什么一圈内一定被追上
把圈展开就行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; ListNode index1 = null ; ListNode index2 = null ; while (fast!=null &&fast.next!=null ){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast==slow){ index1 = fast; index2 = head; while (index1!=index2){ index1 = index1.next; index2 = index2.next; } break ; } } return index1; } }
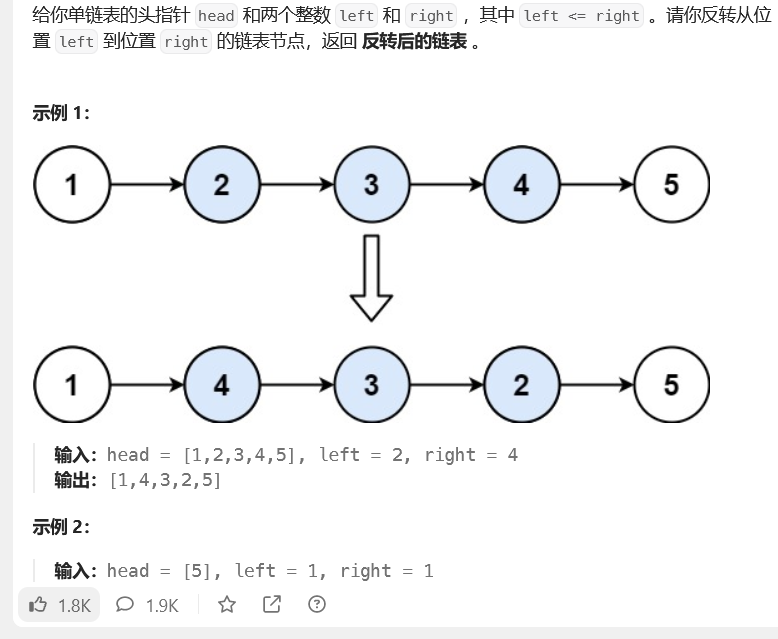
7.反转链表II(leetcode92)
这是小米面试手撕的一道算法,其实我那个想法是正确的,参考了反转链表1,面试官提醒我的是第二种方法。
第二种是穿针引线的方法,pre是不变的,cur其实也是不变的,指向一个节点,只有temp是变的,一直指向cur.next。
然后示例中先是3,2再是4 3 2.最后完成。
下面第一个是我的想法代码,第二种方法是面试官提示我的穿针引线法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 class Solution { public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int left, int right) { if (head.next==null ) return head; ListNode dummy = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode first = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode last = new ListNode (-1 ); dummy.next = head; first = dummy; last = dummy; ListNode pre = dummy; ListNode pre2 = dummy; ListNode cur = dummy; ListNode temp = cur.next; int i=0 ; while (i<left-1 ){ first = first.next; pre = pre.next; pre2 = pre2.next; i++; } pre2 = pre2.next; i=0 ; while (i<right+1 ){ last = last.next; i++; } cur = pre.next; temp = cur.next; i=0 ; while (i<=right-left){ temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; i++; } first.next = pre; pre2.next = last; return dummy.next; } } class Solution { public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int left, int right) { if (head.next==null ) return head; ListNode dummy = new ListNode (-1 ); dummy.next = head; ListNode pre = dummy; int i=0 ; while (i<left-1 ){ pre = pre.next; i++; } ListNode cur = pre.next; ListNode temp = cur.next; int j=0 ; while (j<right-left){ temp = cur.next; cur.next = temp.next; temp.next = pre.next; pre.next = temp; j++; } return dummy.next; } }